Monitoring Blood Sugar: A Key to Successful Diabetes Management
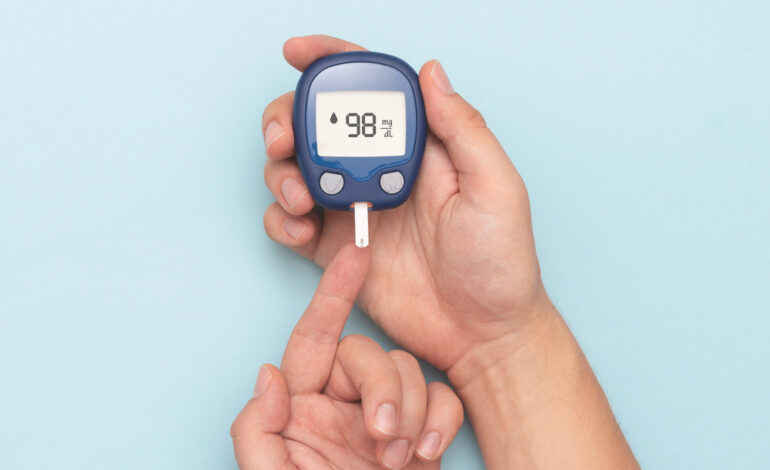
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. It provides vital insights into how well you’re managing your condition and helps you make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of blood sugar monitoring and provide guidance on how to track and interpret your readings effectively.
Why Is Blood Sugar Monitoring Important?
Monitoring blood sugar levels offers several benefits for individuals with diabetes:
- Immediate Feedback: It allows you to see how your body responds to various factors like food, exercise, and medication.
- Treatment Adjustments: By tracking your readings, you can make necessary adjustments to your diet, exercise routine, and medication under the guidance of your healthcare provider.
- Early Detection: Monitoring helps detect and address blood sugar fluctuations before they lead to complications.
- Personalized Management: It allows for personalized diabetes management tailored to your unique needs.
When and How to Monitor Blood Sugar
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring can vary depending on your type of diabetes, treatment plan, and healthcare provider’s recommendations:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Often requires frequent monitoring, including before meals, before bedtime, and sometimes during the night.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Monitoring frequency may range from daily to several times a week, depending on your treatment plan.
Here’s how to monitor your blood sugar effectively:
1. Use a Glucometer: A glucometer is a portable device that measures blood sugar levels. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for accurate readings.
2. Wash Your Hands: Clean your hands thoroughly with soap and water before testing to prevent contamination.
3. Follow a Testing Schedule: Stick to a regular testing schedule to monitor blood sugar at consistent times throughout the day.
4. Record Your Readings: Keep a log of your blood sugar readings. Note the date, time, and any relevant information such as meals, exercise, and medication.
Interpreting Blood Sugar Readings
Understanding your blood sugar readings is essential for making informed decisions. Here are general guidelines for interpreting results:
1. Fasting Blood Sugar (Before Meals):
- Normal: 70-100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 101-125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
2. Postprandial Blood Sugar (1-2 Hours After Meals):
- Target: Less than 180 mg/dL
3. A1C Levels (Average Blood Sugar Over 2-3 Months):
- Target: Less than 7% (individual targets may vary)
It’s essential to discuss target ranges and goals with your healthcare provider, as they may adjust them based on your specific situation.
What to Do When Blood Sugar Is High or Low
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia):
- Stay Hydrated: Drink water to help flush excess sugar from your bloodstream.
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: Take prescribed medications or insulin as directed.
- Review Your Diet: Assess your recent meals for potential triggers of high blood sugar.
- Exercise: Engage in physical activity if it’s safe and recommended by your healthcare provider.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia):
- Consume Fast-Acting Carbs: Eat or drink a source of fast-acting carbohydrates like fruit juice, glucose tablets, or a regular soft drink.
- Recheck Blood Sugar: Wait 15 minutes, then recheck your blood sugar. Repeat the process until it returns to a safe range.
- Eat a Balanced Meal or Snack: After stabilizing your blood sugar, eat a balanced meal or snack to prevent another drop.
Conclusion
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a crucial aspect of successful diabetes management. By tracking your blood sugar levels and understanding the results, you can take proactive steps to maintain optimal control, minimize complications, and lead a healthier life with diabetes.
In the next blog, we’ll explore the significance of diabetes complications, how to prevent them, and the importance of regular medical checkups in diabetes care. Stay informed and empowered on your journey to managing diabetes effectively.










10 Comments
[…] Inhibitors: Lower blood sugar by increasing glucose excretion in the […]
[…] Remember that consistency is key. Make exercise a lifelong habit, and you’ll reap the benefits of improved diabetes management and overall health. […]
[…] managing diabetes is an ongoing journey. Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a registered dietitian or […]
[…] changes that work for you. With dedication and support, you can achieve better control of your diabetes and lead a fulfilling […]
[…] decision-making and better diabetes management. If you have questions or concerns about diabetes, consult a healthcare professional. Diabetes can be well-managed, allowing individuals to lead healthy and fulfilling […]
[…] It Down: Diabetes is not just about managing blood sugar levels; it involves understanding and preventing potential complications that can affect various parts of […]
[…] The blood sample is analyzed for glucose levels. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or higher on two separate tests indicates […]
[…] early intervention and prevention. If you have multiple risk factors or are concerned about your diabetes risk, consult a healthcare professional for guidance. Taking proactive steps, such as maintaining a […]
[…] it’s essential to grasp how this condition impacts your body. Diabetes is not merely about blood sugar levels (Blood Sugar 101); it involves a complex interplay of factors that affect your overall […]
[…] diabetes is the first step toward effective management. If you experience symptoms or have risk factors, […]