Diabetes Risk Factors: Who Is Prone to Developing It?
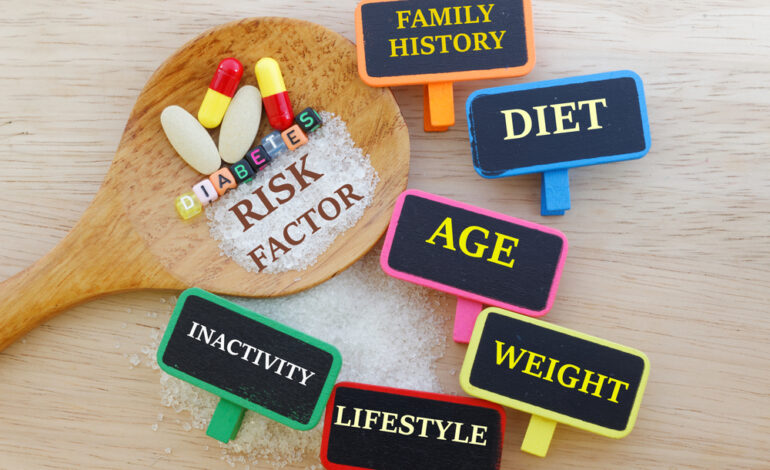

Diabetes does not discriminate. It can affect individuals of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. However, certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing diabetes. By identifying these risk factors, we can better understand who is more vulnerable and take proactive steps to protect our health.
1. Family History
One of the most significant risk factors for diabetes is a family history of the condition. If your parents or siblings have diabetes, your risk increases. This is particularly true for Type 2 diabetes, which has a strong genetic component.
2. Age
Age plays a role in diabetes risk. While Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, Type 2 diabetes is more commonly diagnosed in adults, especially those over the age of 45. However, due to lifestyle factors, Type 2 diabetes is increasingly affecting younger individuals.
3. Weight
Carrying excess weight, especially around the abdomen, significantly increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes. Obesity is closely linked to insulin resistance, a hallmark of this type of diabetes.
4. Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle is a risk factor for diabetes. Lack of physical activity can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance. Regular exercise helps control blood sugar levels and reduces diabetes risk.
5. Diet
Unhealthy eating habits, particularly a diet high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats, can raise the risk of diabetes. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce this risk.
6. Gestational Diabetes
Women who have had gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
7. Ethnicity
Some ethnic groups are more prone to diabetes. For example, individuals of African, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian descent have a higher risk.
8. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women and can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
9. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Having high blood pressure is a diabetes risk factor. It often coexists with other risk factors like obesity and an unhealthy diet.
10. High Cholesterol
Elevated levels of LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and low levels of HDL (“good”) cholesterol can increase the risk of diabetes.
11. Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. It harms the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
12. Stress
Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as overeating or adopting unhealthy coping mechanisms, increasing the risk of diabetes.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early intervention and prevention. If you have multiple risk factors or are concerned about your diabetes risk, consult a healthcare professional for guidance. Taking proactive steps, such as maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and adopting a balanced diet, can reduce your vulnerability to diabetes.